Periodontology is the treatment of periodontitis. Periodontitis is when gums become inflamed.
What causes inflammation of gums to happen?
Step 1. Healthy Gums
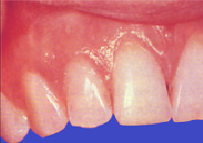
Periodontitis typically always starts with the plaque, food leftovers and bacteria, that are not completely removed when brushing teeth. Healthy gums can become inflamed, and the condition can get worse with time if not treated.
Step 2 – Chronic Gingivitis

Next, plaque spreads out and becomes harder. This leads to tartar build-up, which cannot be removed with a toothbrush. The tartar can cause gingivitis, in which bacteria infect the gums. Chronic gingivitis is a plaque induced inflammatory lesion of the gingiva. Accumulation of dental plaque in the gingival sulcus initiates the development of an inflammatory lesion.
Step 2 – Chronic Gingivitis
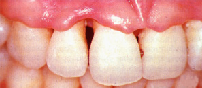
The gums become inflamed, which can cause periodontitis. Chronic periodontitis is bacterially induced inflammation of the periodontium. Approximately 54% of adults have some four mm periodontal pockets present. 5% of adults have pockets of 6mm or greater.
How does periodontology treat inflamed gums?
Treatments can be non-surgical or surgical, depending on the stage of inflammation.
Non-surgical treatments can range from preventive dentistry such as scaling plaque. The best option is to schedule regular preventative dentistry appointments, where the dental clinic will professionally clean hard plaque and advise on proper dental hygiene procedures. However, if further care is necessary following a longer period of inflammation, then other non-surgical procedures include treatments such as root planning or antibiotics.
Surgical treatments include flap surgery, soft tissue grafts or guided tissue regeneration.